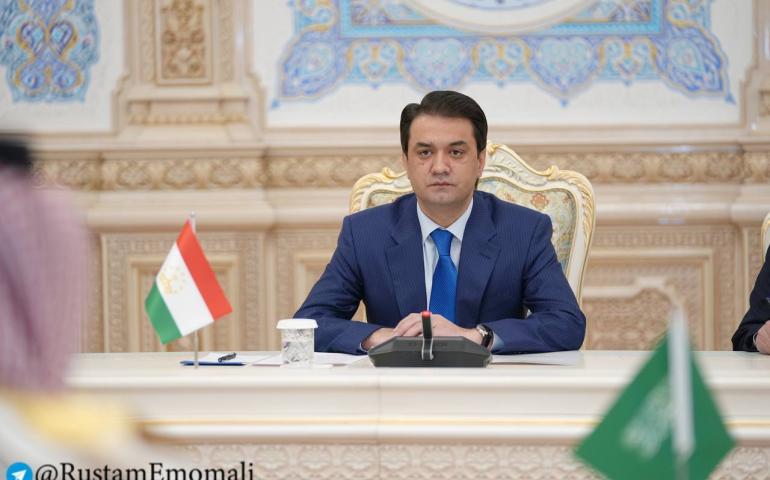
With increasing globalization, states are increasingly faced with foreign interference and pressure in their domestic and foreign policies. Today, most states are “officially” sovereign and face serious pressure from other states, military blocs, political and international organizations.
 With the development of globalization processes, the sphere of action of states is narrowing. In foreign policy, it is almost impossible to create interstate relations without the participation of third countries and international organizations. It is impossible to imagine a conflict between two states without the intervention of a third party. Domestic policy issues go beyond the domestic framework and are taken to the international level.
With the development of globalization processes, the sphere of action of states is narrowing. In foreign policy, it is almost impossible to create interstate relations without the participation of third countries and international organizations. It is impossible to imagine a conflict between two states without the intervention of a third party. Domestic policy issues go beyond the domestic framework and are taken to the international level.
The Constitution of the Republic of Tajikistan is a critical document that establishes the legal and political framework of the country. Adopted on November 6, 1994, it serves as the supreme law, guiding the government’s structure, the division of powers, and the rights and freedoms of the citizens of Tajikistan. The Constitution embodies the principles of democracy, rule of law, social justice, and human rights, which are essential to the country's governance and its citizens' well-being.
Key Significance of the Constitution of Tajikistan:
1. Foundation of State Sovereignty and Independence: The Constitution officially declares Tajikistan as an independent and sovereign state, setting it apart from its past as part of the Soviet Union. This sovereignty is key to the country's identity and allows it to exercise independent domestic and foreign policy.
2. Separation of Powers: The Constitution outlines a government structure based on the principle of separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This system is intended to provide checks and balances that prevent abuse of power and ensure a fair and just governance.
3. Guarantee of Human Rights and Freedoms: Tajikistan's Constitution guarantees various civil liberties and rights, including freedom of speech, freedom of the press, and the right to personal security. These rights are protected to promote individual dignity and provide citizens with fundamental freedoms, though challenges in the application of these rights remain.
4. Establishment of the Rule of Law: As the supreme law, the Constitution enforces the rule of law, meaning that all laws, policies, and governmental actions must align with its principles. This ensures that the government operates within legal boundaries and aims to promote fairness in its interactions with citizens.
5. Stability and Development: The Constitution provides a framework for the country’s long-term political stability and social development. By establishing norms for political participation and governance, it contributes to a stable environment, which is crucial for economic growth and social cohesion.
6. National Unity and Cultural Identity: Emphasizing Tajikistan’s unique cultural heritage, the Constitution also aims to promote national unity and respect for the country's diverse ethnic groups. This commitment to cultural identity plays a significant role in fostering national pride and unity among citizens.
7. Guidance for Amendments and Reforms: The Constitution of Tajikistan includes provisions for its own amendment, allowing it to adapt to changing political, social, and economic conditions. This adaptability is essential for the country’s growth and modernization while remaining aligned with its foundational principles.
Overall, the Constitution of Tajikistan is a vital document that not only defines the structure and functions of government but also sets the vision for the country’s future. It serves as a cornerstone for Tajikistan’s sovereignty, stability, and commitment to upholding the rights and welfare of its people.
Additional Points on the Significance of the Constitution of Tajikistan
1. Framework for Democratic Governance:
Although Tajikistan is a presidential republic, the Constitution establishes a democratic system where leaders are elected, and citizens have the right to participate in government through voting. It outlines the procedures for presidential, parliamentary, and local elections, ensuring that citizens have a voice in the government’s composition. This democratic framework, though with some limitations, plays a key role in fostering civic engagement and political participation.
2. Protection of Social and Economic Rights:
Beyond civil liberties, the Constitution recognizes and safeguards social and economic rights. These include rights to work, social security, education, and healthcare. By addressing these fundamental needs, the Constitution emphasizes the government’s responsibility to protect the well-being and prosperity of its citizens, ensuring a foundation for social stability.
3. Environmental Protection and Resource Management:
The Constitution emphasizes the protection of the natural environment, which is especially relevant for Tajikistan, given its mountainous terrain and reliance on agriculture and hydropower. Article 13 of the Constitution specifically states that natural resources are the property of the state, and their use should consider environmental sustainability. This focus on environmental stewardship aims to protect resources for future generations while addressing current needs.
4. Religious Freedom and Secularism:
Tajikistan's Constitution establishes the country as a secular state, ensuring a separation between religion and government. While it acknowledges the role of Islam and other religions in society, it prohibits the state from enforcing or endorsing any specific religion. This provision helps maintain religious tolerance and freedom, creating a framework for peaceful coexistence among various religious groups.
5. Gender Equality and Women’s Rights:
The Constitution upholds principles of gender equality, ensuring that men and women are equal before the law. It provides a legal foundation to promote women’s rights and counteract discrimination. Although challenges remain in achieving full gender equality, the constitutional commitment to this principle is crucial for promoting women's participation in social, economic, and political life.
6. Guiding Role in Legal System and Judiciary:
The Constitution serves as the cornerstone of Tajikistan’s legal system. It provides the foundation for the development of laws, codes, and regulations governing the judiciary. Judges are expected to interpret and apply laws based on the Constitution’s principles, aiming to ensure fairness and consistency in judicial rulings. The constitutional emphasis on judicial independence is crucial for upholding justice and protecting citizens' rights against potential abuses of power.
7. National Security and Territorial Integrity:
The Constitution asserts Tajikistan’s commitment to preserving its national security and territorial integrity. It emphasizes the role of the state in protecting the nation from external threats and maintaining internal order. In a region with a complex political landscape, this focus on security is vital for Tajikistan’s sovereignty and stability.
8. Foreign Policy and International Cooperation:
The Constitution allows Tajikistan to pursue a peaceful and cooperative foreign policy. It emphasizes respect for international law and treaties, which is important for the country’s diplomatic relations and its integration into the global community. Tajikistan’s Constitution also provides a legal basis for cooperation with international organizations on issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and security.
Amendments and Constitutional Reform
The Constitution of Tajikistan has undergone several amendments since its adoption. These amendments are designed to reflect the changing political, social, and economic context. For example, amendments have been made regarding presidential term limits and the role of political parties. The ability to amend the Constitution allows Tajikistan to adapt to new challenges while preserving core principles.
Conclusion
In summary, the Constitution of Tajikistan is foundational to the country’s identity, sovereignty, and governance. It provides a comprehensive legal and political framework that protects citizens’ rights, supports economic and social development, and promotes democratic values. While challenges remain in fully implementing some of its principles, the Constitution serves as a crucial guide for Tajikistan’s ongoing development as an independent and stable nation.
Thus, the process of globalization affects the sovereignty of the state in both domestic and foreign policy and causes significant changes in the development of the state. In the context of globalization, the issue of possible restrictions on state sovereignty becomes relevant for Tajikistan, which is actively involved in the process of shaping foreign policy and the national economy. In modern conditions, with the increasing influence of factors influencing politics, economics, social life and the ideology of society, the importance of independence for the preservation of language, historical memory, national identity and national culture is extremely important, and the future of the nation and the very existence of the Tajik state can only be stable under political independence.
At the same time, one of the main factors in protecting independence is understanding its significance, studying the historical path traversed by the Tajik people to achieve independence, teaching children and youth the great cultural, literary and scientific heritage of the Tajik people to form national self-knowledge and a sense of patriotism.
As the Founder of peace and national unity-Leader of the nation, the President of the Republic of Tajikistan, His Excellency Emomali Rahmon noted: “In the context of globalization, expanding geopolitical competition, escalation of dangerous manifestations of extremism and terrorism, and other global problems, a thorough study of philosophical, legal, social, political, moral and spiritual views is the need of the time. The study of the material and intangible culture of a nation should be a priority area of scientific research.”
Therefore, we must unite around the Leader of the Nation and act together to develop national statehood and protect independence.
Saidzoda Halim Aziz - Head of the Department of Foreign languages of the National Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan, Doctor of philology, professor